Coronary Angioplasty in Iran
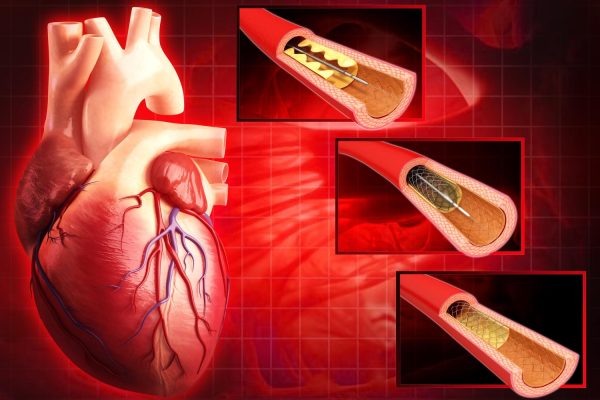
When the blood flow to your heart muscles gets obstructed, it can lead to a heart attack or unbearable chest pain. Coronary Angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to widen narrowed or blocked blood vessels, particularly coronary arteries. During the procedure, a thin catheter with a deflated balloon is inserted into the affected artery. Once in place, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery walls and expanding the vessel to improve blood flow. Proficient Iranian cardiologists use modern techniques to perform effective angioplasty procedures with the best results. Affordable Coronary Angioplasty in Iran is arranged by Iran Medical Tours with the best doctors at modern hospitals in different cities, mainly in Tehran, Shiraz, and Mashad.
Contact Us for a FREE Consultation.
Types Of Angioplasty Surgery
Angioplasty encompasses various techniques designed to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels, primarily the coronary arteries supplying the heart. These procedures aim to restore proper blood flow and can be tailored to specific conditions and patient needs:
-
Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty involves threading a deflated balloon-tipped catheter into a narrowed coronary artery. Upon reaching the blockage, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery walls, widening the vessel lumen, and improving blood flow.
-
Drug-Eluting Stent (DES) Placement: After balloon angioplasty, a stent—a mesh-like tube—is often placed at the site of the blockage. Drug-eluting stents release medication that helps prevent the re-narrowing of the artery (restenosis), reducing the chances of recurrent blockages.
-
Balloon Angioplasty with Cutting Balloon: In certain cases where plaque is resistant to traditional balloon angioplasty, a cutting balloon with small blades on its surface may be used. This device helps modify the plaque, allowing for better artery expansion.
-
Rotational Atherectomy: This procedure involves using a specialized catheter with a rotating tip that shaves off calcified plaque from the artery walls, facilitating balloon angioplasty and stent placement in severely calcified lesions.
-
Atherectomy with Laser or Directional Coronary Atherectomy (DCA): Laser or DCA techniques involve removing plaque using laser energy or a cutting device mounted on a catheter. These methods may be employed in complex cases with hard or calcified plaque.